History Of Communication
Around 200,000 years ago in the era of Homo sapiens, anatomically known as modern human, started the process of communication.
At that time there was no language still our early ancestors, Homo sapiens, managed to evolve and journey across the earth by exchanging and improving their technology by crafting information on the walls of cave and on stones, speeding up the human evolution. Soon after moving in manmade houses and learning languages, we found different ways of sharing information.

One of the famous ways was using the animals and the birds, it not only made the communication faster but also secure. Using such media added an encryption in a message. Birds and animal cannot read our messages neither they can modify or delete it; Training birds and animal was the revolutionary step in sharing information technology. But using same media for multiple messages for multiple locations became challenging.
Each challenges created the window of opportunity for new revolution in communication technologies, as fast we adopted new technologies the time spam between each revolution started decreasing. It took million years to humans to start communicate with each other, but once the communication started there was no end to it.
To mitigate multiple messages for multiple destinations, the postal services were publically established in seventeenth century by Royal mail, where Rome claims to have such services since the beginning of fifteenth century. It was again huge success in the domain of communication, where it reached to the public, and helped us to create road map or transportation map of respective regions.

Developed in the 1830s and 1840s by Samuel Morse (1791-1872) and other inventors, the telegraph revolutionized long-distance communication. It worked by transmitting electrical signals over a wire-laid between stations. In addition to helping invent the telegraph, Samuel Morse developed a code (bearing his name) that assigned a set of dots and dashes to each letter of the English alphabet and allowed for the simple transmission of complex messages across telegraph lines.In 1844, Morse sent his first telegraph message, from Washington, D.C., to Baltimore, Maryland; by 1866, a telegraph line had been laid across the Atlantic Ocean from the U.S. to Europe. Although the telegraph had fallen out of widespread use by the start of the 21st century, replaced by the telephone, fax machine and Internet, it laid the groundwork for the communications revolution that led to those later innovations.

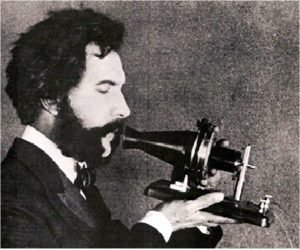
1877-78, we all know that the great Alexander Graham Bell is the father of the telephone. After all it was his design that was first patented; however, he was not the first inventor to come up with the idea of a telephone. The first telephone line was constructed, the first switchboard was created and the first telephone exchange was in operation. Three years later, almost 49,000 telephones were in use.
And, with the help of all best brain and logic in the world the first computer has borne. The development of electronic computers had clearly helped to visualize the concept of communication. The computer system has taken a big leap forward with each technological breakthrough during the development process. The functions performed by the computers and speed of their operations have been changing. Technological breakthrough in hardware and software resulted into more and more advanced computer system belonging to one particular technological class is said to belong to a particular computer generation.

And, the last but not least; way back all before above invention “Zero” was discovered in India as the place value in number system by Indian mathematician Aryabhata. Yes you read it right, India was the first country to accept zero in their number system. The credit for the invention of zero goes to Indian mathematicians and the number zero first appears in a book about ‘arithmetic’ written by an Indian mathematician Brahamagupta.

Also, modern world’s binary system is advanced version of Pingala’s Chandaḥśāstra. Use of zero is sometimes ascribed to Pingala due to his discussion of binary numbers, usually represented using 0 and 1 in modern discussion, but Pingala used light (laghu) and heavy (guru) rather than 0 and 1 to describe syllables. Pingala used the Sanskrit word śūnya explicitly to refer to zero. Without invention of 0 and binary number we would have not able to make today’s world Digital world. Will see later in book how does the Binary system work.
In 1957, IBM developed FORTRAN.
In 1959, Integrated Circuit(IC) came into existence which was later used in the computers.
In 1960, Mainframe computer was designed which used IC for the first time.
In 1970, Memory chip with 1KB storage capacity was developed by Intel.
In 1975, First micro-computer was developed by H. Edward Roberts
In 1980’s and 1990’s, many modifications and up-gradations were done and the usage of chips and various other stuffs changed the computers completely. Before this technologies and innovation goes publically the question raised was who will decide which device, which product and which technologies to be used by public, there has to be some standards and safety regulations.
Around 1945, after the end of World War II, the International Federation of the National Standardizing Associations (ISA) was approached by the recently formed United Nations with a proposal to form a new global standards body. In October 1946, ISA and UNSCC delegates from 25 countries met in London and agreed to join forces to create the new International Organization for Standardization; the new organization officially began operations in February 1947. Same like ISO many other non-profitable organisation been formed to provide standards to product and technologies, some of them are
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI) ansi.org
- Electronics Industries Association (EIA) eia.org
- Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) ieee.org
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO) iso.org
- International Telecommunications Union (ITU) itu.int
Each, of such organisation plays very important role in standardizing products and technologies. As a Network Administrator it is good to have knowledge of standardization, for more details to find out more about this organisation and what type of technologies or products are standardised by them visit above links.
“Our Need predicts the Future and builds it in Present”
-Naresh Rathod
In the May 1970 issue of Popular Science magazine Arthur C. Clarke was reported to have predicted that satellites would one day “bring the accumulated knowledge of the world to your fingertips”

During the early 1980s, there was a married couple namely Len and Sandy Bosack who used to work in two different departments of computer, located in Stanford University. This couple was facing problem in making their computers communicate with each other. In order to overcome this problem, they made a gateway server in their living room which led to a simpler way of making two departments communicate each other by the help of IP protocol.
They founded cisco Systems (with small c) in 1984, having a small commercial gateway server which brought a revolution in Networking. These two Stanford University computer scientists, who pioneered the concept of a local area network (LAN) being used to connect geographically disparate computers over a multiprotocol router system, by the time the company went public in 1990, when it was listed on the NASDAQ, Cisco had a market capitalization of $224 million. Cisco was the most valuable company in the world by 2000, with a more than $500 billion market capitalization.
Due to such huge success and demand cisco system not only produces finest devices, but also produces great network engineers by providing them best industrial training in the subject of network communication. When I started my journey I started as a Network Engineer and then a project manager and due to some of the projects demand I started providing training after becoming CCSI (Cisco Certified System Instructor), and that was one of the reasons which motivated to write a technical book on network communication. I will be sharing as much as knowledge possible. Let’s DIVE! And start our journey…………………………


